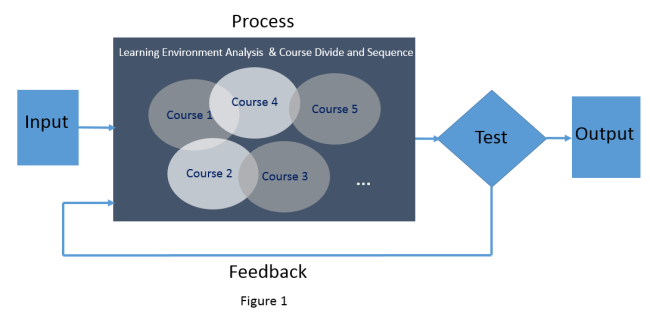
Input: Anything used in Process phase, including information, resources (human & material) and ideas. In this context, it refers to predetermined National College English Syllabus, some existing learning materials (textbooks, video & audio, etc.) and data of students’ learning outcomes (e.g. grades in CET & course final exams)
Process: Actions taken in this stage to do something with information gained in Input phase. It involves a series of activities. It is a process of developing curriculum based on requirements and analysis results. Overlap parts indicates that courses are interconnected with each other. One course might be the perquisite of another one or there is consistency in contents. Therefore, instructional designers should pay attention to individual course as well as relations between courses (e.g. sequence, content) .More details in each oval will be specified in figure 2. Before jumping in level 2 development (course-level), some issues need to be considered: overall learning environments features, how to divide courses, in what sequence do we arrange them.
Test & Feedback: The test stage provides opportunity to examine the validity and credibility of all courses developed and the effectiveness of the curriculum as a whole. Focus group or pilot group can be used. One approach is gathering data of focus group’s performance in CET to see where there is room for improvement. Thereby feedback informs us to revise the project. It is an ongoing process.
Output: Output in this model refers to final products of the project. In this curriculum-oriented context, it covers several things: modification or creation of textbooks and related learning materials; individual course that is fully developed in every aspect (e.g. strategies, delivery, evaluation instruments; how it can be related to other courses…)
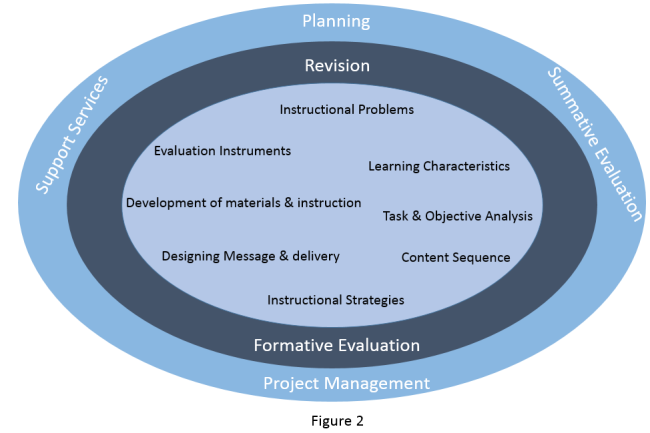
Figure 2, whose origin is from Kemp, Morris & Ross Model, represents the process of developing an individual course across the curriculum.
Analysis:
Instructional problems—based on data gathered in Input stage, identify instructional problems and specify goals for developing this course
Learner characteristics—Examine students characteristics that should receive attention during planning; it should be noted that arts students and science & engineering students usually hold different attitudes and expectations towards English learning.
Task &Objective analysis—Identify subject contents, and analyze task components related to stated goals and objectives( alignment).
Design:
Content sequence—sequence content with each instructional unit for logic learning.
Instructional strategies—design appropriate instructional strategies to help learners master learning objectives.
Design messages & instructional delivery—planning instructional message and ways to deliver
Development:
Development of instruction and materials—develop the overall instruction; creating materials to support instruction or activities or selecting existing materials.
Evaluation:
Evaluation instruments—develop evaluation tools to assess learning outcomes.
Revision and Formative Evaluation: a continuous and ongoing process; a variety of techniques & strategies can be used to conduct the evaluation such as pilot groups.
Planning, Summative Evaluation, Support Services and Project Management: an emphasis on how to manage the instructional design process.
Oh interesting. I like the model with the specific course development model within the curriculum development model.